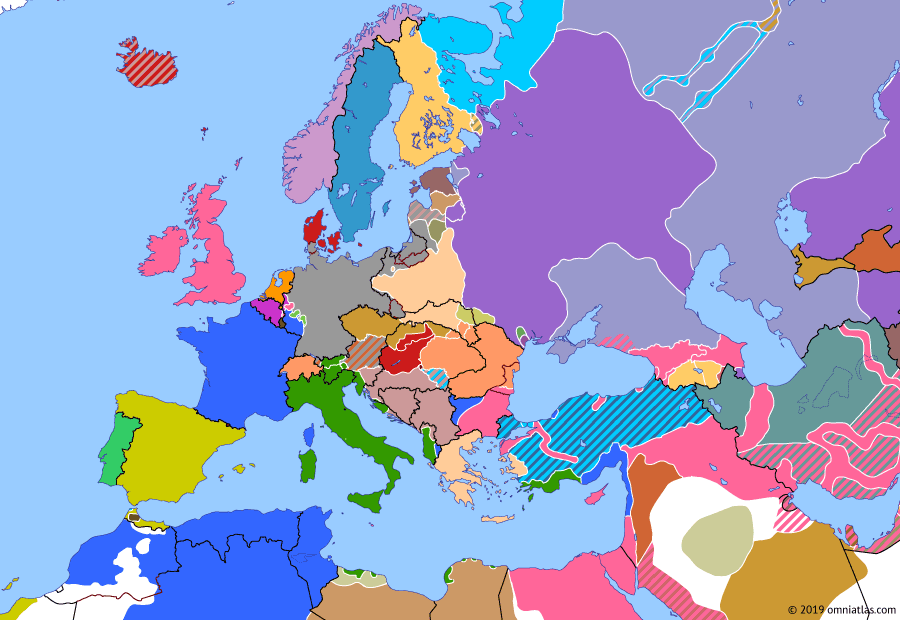
Europe 1919: Treaty of Versailles
28 June 1919
28 Jun 1919
Armistice Europe
-27–68 Julio-Claudian Dynasty
68–96 Flavian Dynasty
96–192 Nerva–Antonine Dynasty
192–235 Severan Dynasty
235–268 Crisis of the Third Century: Turmoil
268–284 Crisis of the Third Century: Restoration
284–311 Diocletian and the Tetrarchy
311–363 Constantinian Dynasty
363–383 Valentinianic Dynasty
383–408 Theodosian Dynasty: Divided Empire
408–425 Theodosian Dynasty: The West Besieged
425–441 Theodosian Dynasty: Fall of Africa
441–457 Theodosian Dynasty: Hunnic Wars
457–1803 NO MAPS FOR THIS PERIOD YET
1803–1814 Napoleonic Wars
1814–1815 Vienna and Waterloo
1815–1848 Congress Europe
1848–1850 Springtime of Peoples
1850–1859 Crimean War
1859–1862 Italian Unification
1862–1871 German Unification
1871–1914 Imperial Europe
1914–1918 Great War
1918–1922 Armistice Europe
1922–1939 Rise of Fascism
1939–1942 World War II: Blitzkrieg
1942–1945 World War II: Fall of the Third Reich
1945–1990 Cold War
1990–2010 Post-Cold War Europe
2010–pres Crisis of Europe
Treaty of Versailles
4 Dec 1918 New Countries in Eastern Europe
10 Jan 1919 January Revolt in Germany
9 Apr 1919 Specter of Communism
28 Jun 1919 Treaty of Versailles
10 Sep 1919 Treaty of St. Germain
27 Nov 1919 Treaty of Neuilly
6 Apr 1920 Allies Under Pressure
4 Jun 1920 Treaty of Trianon
10 Aug 1920 Treaty of Sevres
12 Nov 1920 Treaty of Rapallo
20 Mar 1921 Limits of Soviet Expansion
23 Aug 1921 Greco-Turkish War
28 Jun 1922 Irish Civil War
While Europe united to crush Communism, the Allies imposed the Treaty of Versailles on Germany. The effects of this Treaty were to: restrict Germany's ability to wage war; force Germany to pay huge reparations for the War; surrender German territory to France, Belgium, and Poland; make Danzig a free city; and create plebiscite zones with Denmark and Poland (where the local people would later vote for which country they would belong to).