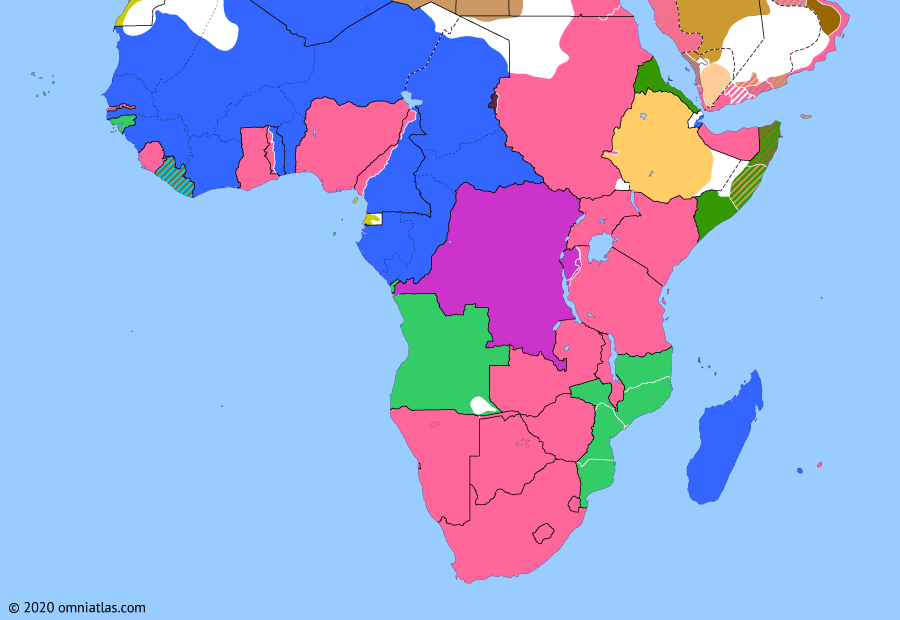
Sub-Saharan Africa 1920: Africa and the Peace Treaties
10 August 1920
10 Aug 1920
Africa and the Peace Treaties
10 Aug 1920 Africa and the Peace Treaties
20 Jul 1922 League of Nations Mandates
15 Jul 1924 Anglo-Italian Convention
16 Nov 1925 Campaign of the Sultanates
27 Apr 1929 Trans-African Routes
17 Apr 1931 Africa during the Great Depression
16 Jan 1935 Abyssinia Crisis
9 May 1936 Second Italo-Ethiopian War
4 Feb 1939 Spanish Civil War in Africa
Fighting continued in East Africa for a few days after the end of World War I in Europe, until news of the Armistice finally reached German General Lettow-Vorbeck in Northern Rhodesia and he agreed to surrender. At the treaties of Versailles and Sèvres, the Germans and their Ottoman allies accepted the loss of their empires.