Sub-Saharan Africa 1942: Occupation of Madagascar
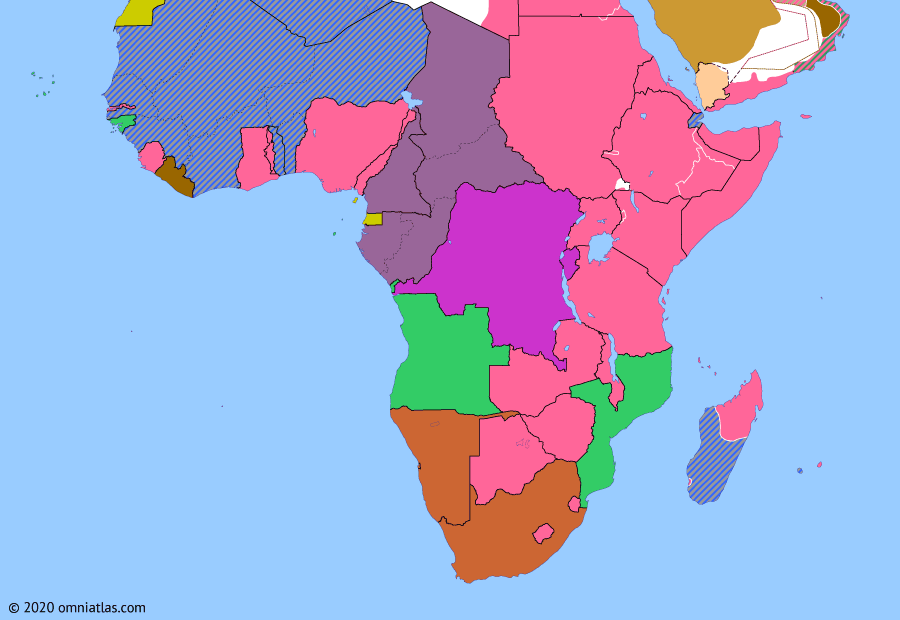
29 September 1942
29 Sep 1942
Occupation of Madagascar
24 Jun 1940 World War II and the Fall of France
19 Aug 1940 Italian East African Offensives
25 Sep 1940 Debacle at Dakar
8 Nov 1940 Battle of Gabon
1 Mar 1941 East African Campaign
6 Apr 1941 Liquidation of Italian East Africa
7 May 1942 Operation Ironclad
29 Sep 1942 Occupation of Madagascar
23 Nov 1942 Three French Empires
3 Jun 1943 French Committee of National Liberation
25 Aug 1944 From Africa to Paris
15 Aug 1945 End of World War II
The British capture of Diégo Suarez in May 1942 did not completely remove the Japanese threat to Vichy Madagascar. In September the British moved south to occupy the rest of the island, taking the capital of Tananarive on the 23rd and receiving the final Vichy French surrender in November.