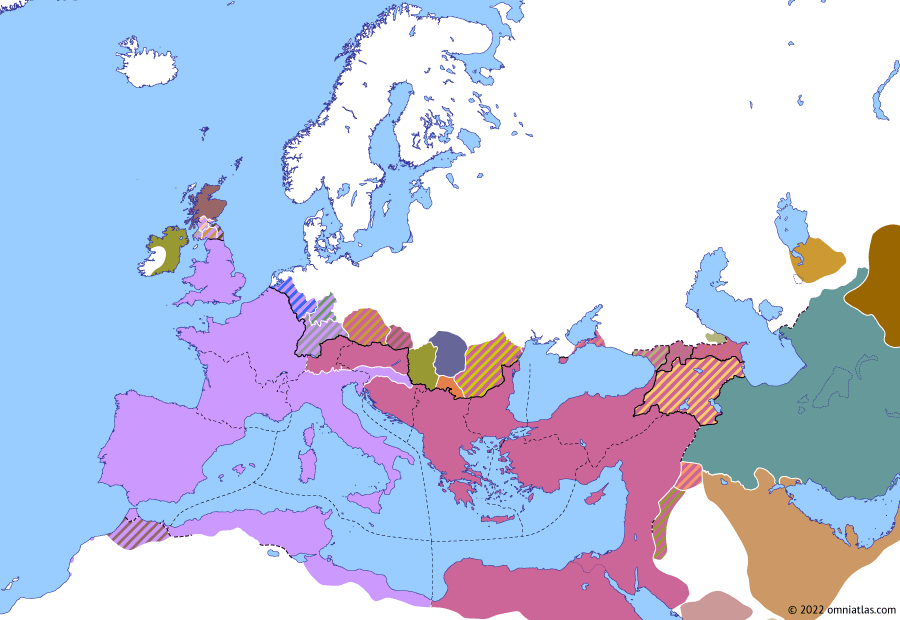
Europe 316: Battle of Cibalae
8 October 316
8 Oct 316
Constantinian Dynasty
-27–68 Julio-Claudian Dynasty
68–96 Flavian Dynasty
96–192 Nerva–Antonine Dynasty
192–235 Severan Dynasty
235–268 Crisis of the Third Century: Turmoil
268–284 Crisis of the Third Century: Restoration
284–311 Diocletian and the Tetrarchy
311–363 Constantinian Dynasty
363–383 Valentinianic Dynasty
383–408 Theodosian Dynasty: Divided Empire
408–425 Theodosian Dynasty: The West Besieged
425–442 Theodosian Dynasty: Fall of Africa
442–1803 NO MAPS FOR THIS PERIOD YET
1803–1814 Napoleonic Wars
1814–1815 Vienna and Waterloo
1815–1848 Congress Europe
1848–1850 Springtime of Peoples
1850–1859 Crimean War
1859–1862 Italian Unification
1862–1871 German Unification
1871–1914 Imperial Europe
1914–1918 Great War
1918–1922 Armistice Europe
1922–1939 Rise of Fascism
1939–1942 World War II: Blitzkrieg
1942–1945 World War II: Fall of the Third Reich
1945–1990 Cold War
1990–2010 Post-Cold War Europe
2010–pres Crisis of Europe
Battle of Cibalae
28 Oct 312 Battle of the Milvian Bridge
30 Apr 313 Battle of Tzirallum
8 Oct 316 Battle of Cibalae
1 Mar 317 Peace of Serdica
May 323 Licinius and the Goths
18 Sep 324 Battle of Chrysopolis
11 May 330 Foundation of Constantinople
late 332 Roman Gothia
sum 336 Constantine’s Dacia
9 Sep 337 Sons of Constantine
Apr 340 Battle of Aquileia
sum 346 Nisibis War
18 Jan 350 Magnentian Revolt
3 Jun 350 Vetranio and Nepotian
28 Sep 351 Battle of Mursa Major
3 Jul 353 Battle of Mons Seleucus
11 Aug 355 Silvanus
24 Jun 356 Julian’s Gallic Wars
sum 357 Battle of Strasbourg
Feb 360 Usurpation of Julian
3 Nov 361 Death of Constantius II
29 May 363 Julian’s Persian Campaign
Three years after the downfall of Maximinus Daza, the alliance between Constantine and Licinius broke down. Constantine invaded Licinius’ territory in the fall of 316, defeating him at Cibalae, near Sirmium, in early October.